Appendix G: DD Command for Image Backup
Step 1: Introduction
Data loss will be costly. At the very least, critical data loss will have a financial impact on companies of all sizes. There are several ways to back up a Linux system.
This section provides practical examples on using dd command to back up the Linux system. dd is a powerful UNIX utility. It can also be used to copy data. Only super user can execute dd command.
Step 2: Image Backup
Suppose M.2 SATA disk has Linux OS and need to have a backup of the Linux OS image.
Connect the SATA drive in development PC by using M.2 SATA to USB cable or if you don’t have the cable, boot the target board with some other hard disk (m-SATA port) where the M.2 SATA drive will be detected as external memory card.
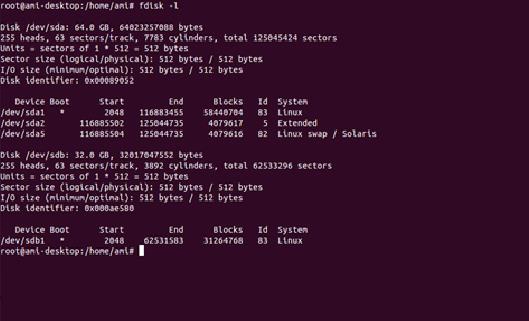
Become a root user and enter following command in terminal
$fdisk –l
It will appear as follows
From the above window .It is clear that /dev/sdb is the M.2 SATA drive (32.0GB).
Use the following command to take Linux image backup.
$ dd if=/dev/sdb of=Linux_Backup_image.img Where if is input file, of is output file
It will take minimum 15 minutes. And the img file will be saved in current directory.
Step 3: Image Restore
The image restoring medium must have same size as original medium.
Insert the restoring medium and it must be formatted in FAT format.
Use fdisk –l command to know your restoring medium. Ex /dev/sdb or /dev/sdc
Once you found your device .Use the following command to restore the image
Change your directory where the img file saved and run the following command $ dd if= Linux_Backup_image.img of=/dev/sdb
It will take minimum 15 minutes and once done, the medium is ready to boot the OS.
Last updated