Step 3: Graphics Configuration File Setup
In the putty terminal, enter the command “drm-intel” and then “drm-probe-displays” for checking the connected display devices.
# drm-intel
Once this command got executed QNX machine screen gets blank.
# drm-probe-displays
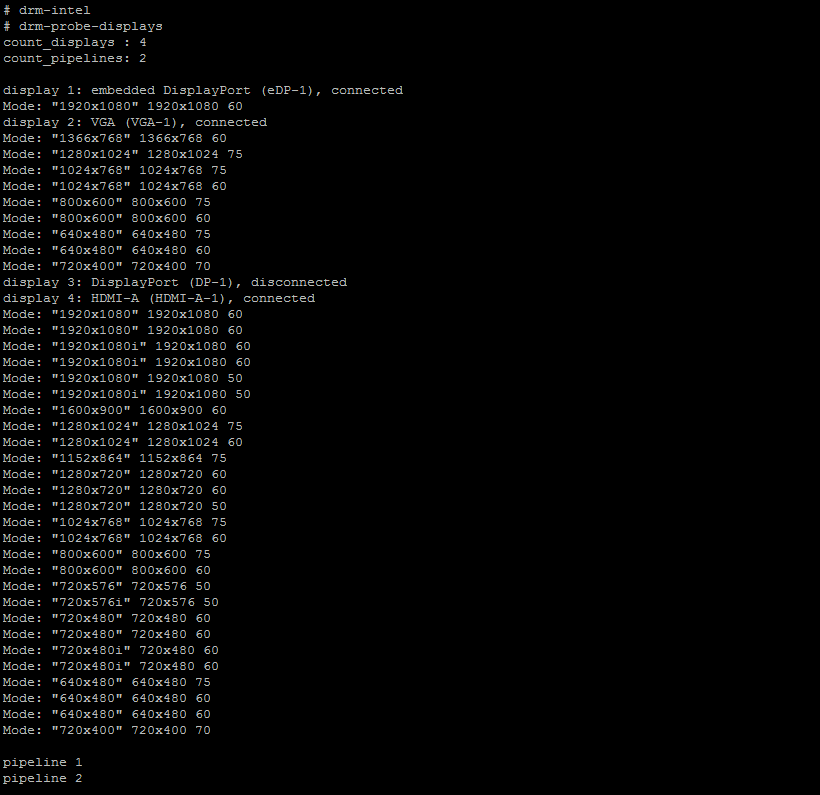
Executing the above command displays the devices display name and its display number as shown in the image below. Here all the display devices has been connected and enabled in BIOS setup as shown in Step1.
Here,
Display 1 - Embedded Display Port is LVDS and its shown the supported display resolution modes. Display 2 - VGA display connected and its shown the supported display resolution modes. Display 3 - Display Port not connected. Display 4 - HDMI-A which is HDMI connected devices and its shown the supported display resolution modes.
Inorder to run the graphic applications, we have to setup the graphics configuration file based on the connected devices display numbers. Graphic configuration file will be present on the “/lib” path with the name of graphics.conf.
# cd /lib/
Here you can able to see the config file graphics.conf using “ls” command.
Copy the config file through USB and change the configurations as given in the steps below.
Open the config file using NotePad++ application in host machine. Below config file format will have LVDS and VGA display combinations.
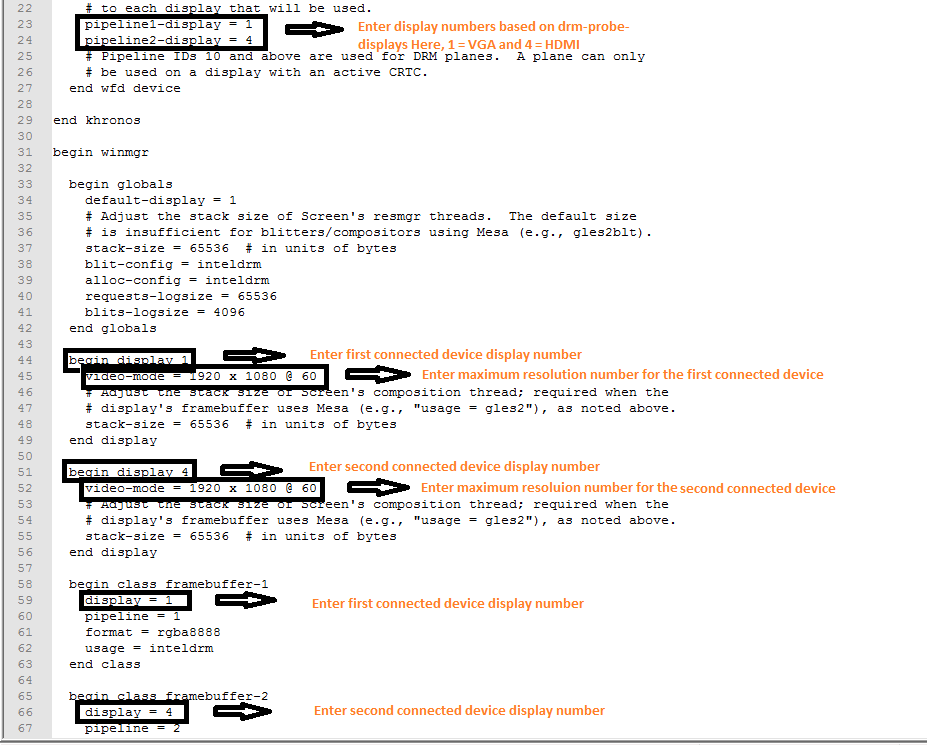
Above commands should be changed according to drm-probe-displays.
In the BIOS setup if we are disabling the LVDS display then “drm-probe-display” shows Display 1 for VGA then change the commands in the config file as shown in the image below.
For example, Below image has been configured according to VGA and HDMI combinations.
Once the configuration changes has been done, save the file and replace the file in QNX system in the same path of /lib/graphics.conf
Note: Don’t change the conf file name. It should be graphics.conf
Last updated